Description
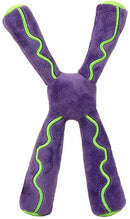
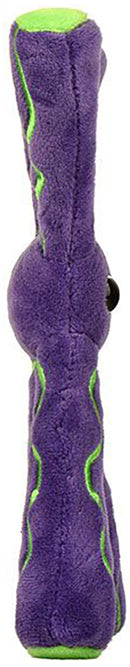
Giant Microbes Plush - Chromosome
These Giant Microbes Dolls are a Million times their Actual Size! GIANT microbes are health and science products for humorous, educational, collectible and Smart fun! Products include printed cards with fun fascinating facts. Unique gifts for students, scientists, teachers, health professionals & anyone with a healthy sense of humor!
All About Chromosome
Chromosomes are threadlike structures inside of cells that store genetic information. They are composed of the material chromatin, which consists of DNA, RNA and proteins. Most human cells have two pairs of 23 chromosomes, one pair from your mother and the other from your father, for a total of 46 chromosomes.
Great gift for anyone who wants to know who they are and what they're made of.
FACTS: Chromosomes are threadlike structures inside of cells that store genetic information. They are composed of the material chromatin, which consists of DNA, RNA and proteins. Most human cells have two pairs of 23 chromosomes, one pair from your mother and the other from your father, for a total of 46 chromosomes.
In the 1890s Theodor Boveri was the first to propose that genes resided in coiled filaments found in the nucleus of cells. He discovered these structures by staining sea urchin cells with blue dye. Thus, “chroma” or color is the basis of the word chromosome.
The DNA within chromosomes contains the genetic code that describes the physical characteristics of every known life form. DNA is so tightly wound in each chromosome that the entire human genetic code of 3 billion base pairs fits in an area of just 6 microns, 10 times smaller than the diameter of hair! The coiling of DNA into chromosomes not only saves space, but also allows the DNA to be replicated more accurately.
The ends of chromosomes are marked with DNA sequences called telomeres. These are like plastic tips at the ends of shoelaces, protecting chromosomes from fraying and degenerating. It is intriguing that scientists believe that telomeres are associated with aging. Each time a cell divides during your lifetime, the DNA’s genetic code is copied. But the telomeres cannot be completely copied, as some bits are cut off. They get shorter over time. As we age, cells with shorter telomeres are unable to replicate, leading to tissue damage and the signs of aging. Older people may be big in stature, but tend to get shorter in height and have shorter telomeres.
Payment & Security
Payment methods
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Security